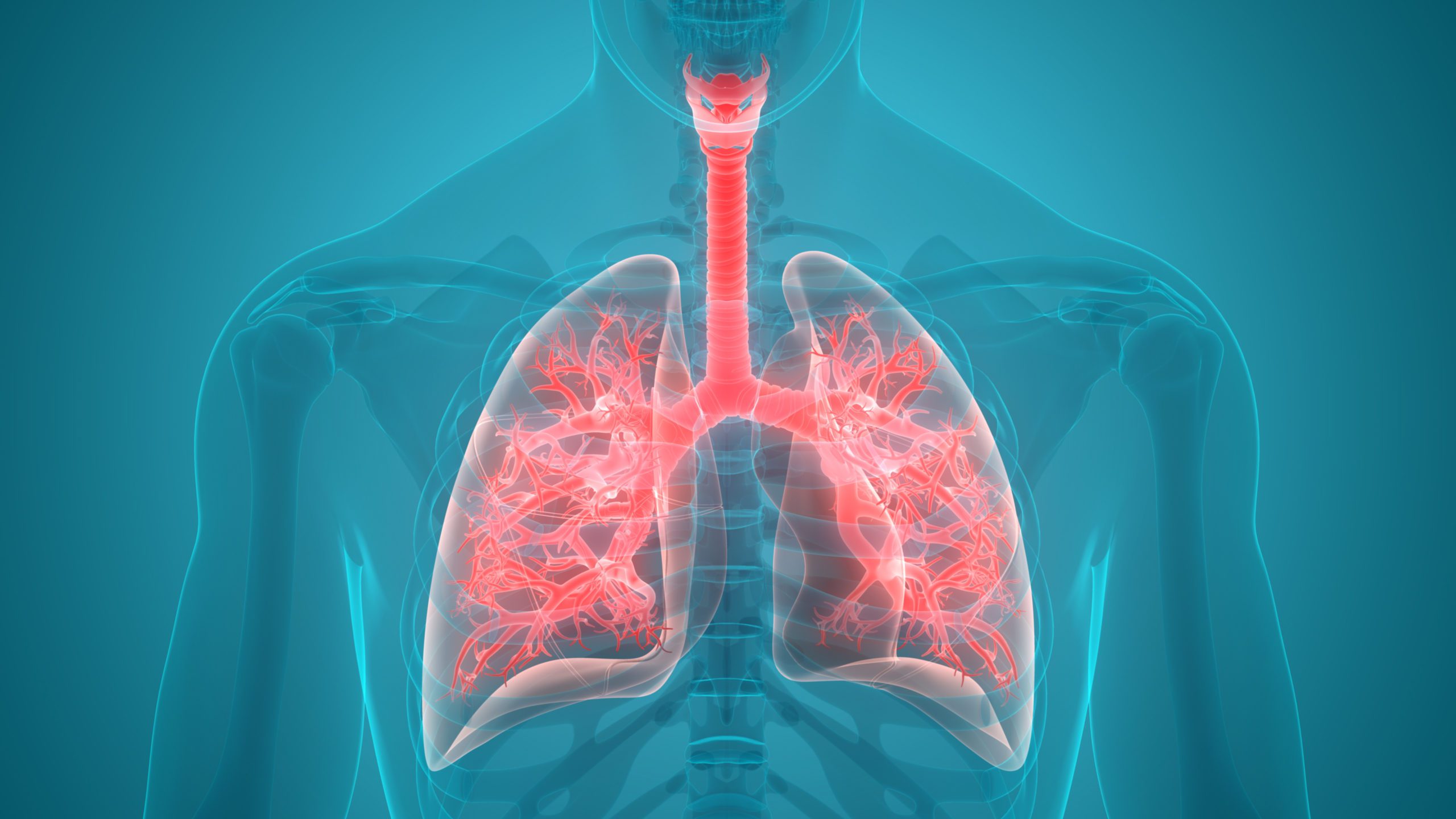
Pneumonia is an infection of lungs that can cause mild to severe illness in people of all ages. It is a leading cause of death worldwide, particularly in children and older adults. Pneumonia can be caused by different micro orgnisms like bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms and can range in severity from mild to life-threatening illnesses.
8 Symptoms of pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the individual’s cause, severity, and underlying health. Common symptoms include:
- Cough that produces phlegm or mucus: This is often a persistent cough that produces thick, yellow, green, or bloody mucus.
- Shortness of breath: This can range from mild to severe and may be more noticeable when exercising or performing activities that require more physical effort.
- Chest pain or discomfort when breathing deeply or coughing: This can be a sharp or dull pain that is felt in the chest or ribs.
- Fever, sweating, and chills: A fever is typically defined as a body temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher and is often accompanied by sweating and chills.
- Fatigue: Pneumonia can cause extreme fatigue and weakness, making it difficult to perform everyday activities.
- Muscle aches: Pneumonia can cause muscle and body aches, which may feel like a flu-like symptom.
- Loss of appetite: Pneumonia can cause a loss of appetite and a decrease in appetite, leading to weight loss.
- Nausea and vomiting: Pneumonia can cause nausea and vomiting, leading to dehydration.
In severe cases, pneumonia can cause confusion, difficulty speaking, or a bluish tint to the skin due to a lack of oxygen.
Diagnosis:
If you suspect you or a loved one may have pneumonia, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. A physical examination, chest x-ray, and laboratory tests can help confirm the diagnosis of pneumonia. Your doctor may also recommend additional tests, such as a CT scan or bronchoscopy, to determine the cause and severity of the infection.
Causes:
Pneumonia is usually caused by bacteria or different viruses that enter the lungs and multiply, causing inflammation and filling the air spaces with fluid. The most common cause of bacterial pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumonia, but other bacteria can also cause the infection. The influenza virus usually causes viral pneumonia, but other viruses, such as the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and adenovirus, can also cause pneumonia.
Risk factors:
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing pneumonia, including:
- Age: Children under 2 and adults over 65 are at higher risk of developing pneumonia.
- Weakened immune system: People with HIV/AIDS, cancer or other conditions that weaken the immune system are at higher risk of developing pneumonia.
- Chronic illnesses: People with chronic illnesses such as asthma, diabetes, and heart disease are at higher risk of developing pneumonia.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the respiratory system and can increase the risk of pneumonia.
- Poor nutrition: Malnutrition can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of pneumonia.
Prevention:
Several measures can be taken to reduce the risk of developing pneumonia:
- Get vaccinated: Pneumonia vaccines are available for adults and children and can help prevent certain types of pneumonia.
- Practice good hygiene: Washing your hands regularly and covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze can help prevent the spread of pneumonia.
- Avoid close contact with sick people: Avoiding close contact with people who are ill can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages the respiratory system and increases the risk of pneumonia. Quitting smoking can help protect against pneumonia and other respiratory diseases.
Treatment:
The treatment of pneumonia depends on the individual’s cause, severity, and underlying health. Mild cases of pneumonia may be treated with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and relieve symptoms. More severe cases may require hospitalization and treatment with antibiotics or antiviral drugs. Oxygen therapy may also be necessary in severe cases to help improve oxygen levels in the blood.
Conclusion:
Pneumonia is a common and potentially serious infection of the lungs that can affect people of all ages. It is important to be aware of the risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures for pneumonia and to seek medical treatment if necessary. Vaccination and good hygiene practices can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia. With proper treatment, most people with pneumonia recover fully.
Home Care for pneumonia
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with pneumonia, “From the Heart Home Care” can help. Our team of trained and compassionate caregivers is here to provide personalized home care services to help you or your loved one recover from pneumonia in the comfort of home. We offer assistance with daily activities such as bathing, dressing, and grooming, as well as help with medication management and providing nutritious meals. We also provide emotional support and companionship to help our clients feel less isolated during their recovery. Don’t struggle through pneumonia alone, contact us today to learn more about how we can help you or your loved one on the road to recovery.
Home Care Near Me. Let’s Get Started!
Get Immediate Help with Information, Costs & Payment Options.